Difference between NMOS PMOS and CMOS transistors
Difference between NMOS PMOS and CMOS transistors
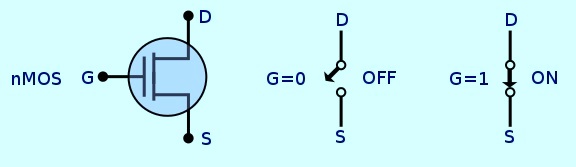
NMOS
is constructed with the n-type source and drain and a p-type substrate, while
PMOS is constructed with the p-type source and drain and an n-type substrate.
In an NMOS, carriers are electrons, while in a PMOS carrier are holes. Where
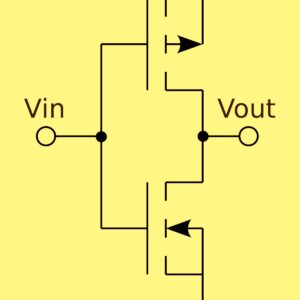
CMOS is the combination of NMOS and PMOS. CMOS technology uses less energy to
operate at the same output and produces less noise during operation.
There are two most popular MOS (Metal Oxide Semiconductor) technologies namely CMOS and NMOS which are widely used in the field electronics and power electronics such as in ASICs, memories, processors, etc. Nowadays, the CMOS technology is one of the leading semiconductor technology. It is because the CMOS technology dissipates less power when compared to the bipolar and NOMOS technology.

In this tutorial, we will discuss the major differences between CMOS technology and NMOS technology. But before discussing the differences, let's get a brief overview of what the CMOS and NMOS technologies are.
What
is NMOS?
NMOS
(nMOSFET) is a kind of MOSFET. An NMOS transistor consists of n-type source and
drain and a p-type substrate. When a voltage is applied to the gate, holes in
the body (p-type substrate) are driven away from the gate. This allows the
formation of an n-type channel between the source and the drain, and a current
is conducted from electrons from the source to the drain through an induced
n-type channel.
Logic
gates and other digital devices implemented using NMOSs are said to have NMOS
logic. There are three operating modes in a NMOS called cut-off, triode and
saturation. NMOS logic is easy to design and manufacture. Circuits with NMOS
logic gates, however, consume static power when the circuit is idle, since DC
current flows through the logic gate when the output is low.
NMOS is the abbreviation used for N-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor. The NMOS uses N-type semiconductor material as the source and drain and a P-type semiconductor material as the substrate.
The NMOS technology is used to design a variety of microelectronic circuits that are used in logic chips and memory chips and also it is used as the part of CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) design.
In an NMOS, there is a layer, called N-channel layer, which conducts electrons between source and drain terminals. The NMOS technology is widely used in microprocessors and many other metal oxide semiconductor devices because they need smaller chip region and gives high density. Also, the NMOS technology gives high speed because they have electrons as the charge carriers that have relatively high mobility.
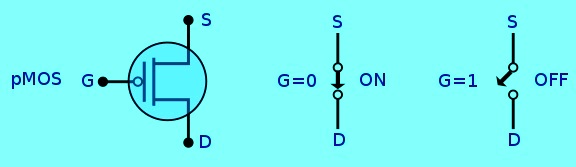
PMOS
(pMOSFET) is a MOSFET type. A PMOS transistor consists of a p-type source and
drain and an n-type substrate. When a positive voltage is applied between
source and gate (negative voltage between gate and source), a p-type channel
with opposite polarities is formed between source and drain. A current is
passed through holes from the source to the drain through a p-type induced
channel.
A
high voltage at the gate causes a PMOS to not conduct, while a low voltage at
the gate causes it to conduct. Logic gates and other digital devices
implemented using PMOS should have PMOS logic. The PMOS technology is
inexpensive and has good immunity to interference.
What
is CMOS?
Complementary
Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (CMOS) is an integrated circuit technology. CMOS
technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, static RAM and other
digital logic circuits.
The
CMOS technology is also used for various analog circuits such as image sensors
(CMOS sensor), data converters and highly integrated transceivers for many
types of communication.
CMOS stands for Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor. The CMOS technology is widely used in manufacturing of ICs, digital logic circuits, microprocessors and microcontrollers, memories, etc. The CMOS technology is a combination of PMOS and NMOS technology.
The CMOS technology is one of the leading semiconductor technology because it consumes low power and has high immunity against electronic noise. Basically, the CMOS or Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor is an onboard semiconductor chip power by a battery and is used for data storage in computing devices. In a typical computer system, the system time and date and other hardware settings of a computer system are maintained by the CMOS IC.
The major advantage of a CMOS device is that it uses electrical power more efficiently. The other primary advantages of CMOS are as −
- It reduces the complexity of the circuit.
- It has high immunity against noise.
- It produces less heat.
- It has very low static power consumption.
- CMOS provides high density of logic functions on a single chip.
The CMOS technology is used in microprocessors, microcontrollers, memories, and many other digital logic circuits and analog circuits like data converters, sensors, communication devices, etc.
The
difference between NMOS, PMOS and CMOS transistors
NMOS:
- NMOS consists of n-type source and drain and a p-type substrate.
- In an NMOS, carriers are electrons When a high voltage is applied to the gate, the NMOS conducts If there is a low voltage at the gate, the NMOS will not conduct NMOS are said to be faster than PMOS because the charge carriers in NMOS, which are electrons, travel twice as fast as holes.
- NMOS ICs would be smaller than PMOS ICs NMOS can deliver half of the impedance delivered by a PMOS NMOS represents an N-type MOS transistor.
PMOS:
- PMOS is constructed with p-source and drain and an n-substrate.
- PMOS, carriers are holes. If a high voltage is applied to the gate, the PMOS will not conduct When a low voltage is applied to the gate,
- PMOS conducts Which are the carriers in PMOS.
- PMOS devices are less susceptible to interference than NMOS devices. PMOS represents a P-type MOS transistor.
CMOS:
- CMOS means complementary metal oxide semiconductor transistor.
- The CMOS circuit includes a PMOS transistor and an NMOS transistor.
- CMOS is more of a term from process technology.
- Top of Form
- Bottom of Form
Difference between CMOS and NMOS Technology
Both CMOS and NMOS are widely used metal oxide semiconductor technologies in microelectronic circuits. However, there are several differences between CMOS and NMOS that are listed in the following table:
| Basis of Difference | CMOS Technology | NMOS Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Full form | CMOS stands for Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor. | NMOS stands for N-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor. |
| Definition | A metal oxide semiconductor technology that combines both PMOS and NMOS technologies is called CMOS. | A metal oxide semiconductor technology that uses N-type channel between source and drain terminals is called NMOS. |
| Operation | The CMOS performs its operation by employing symmetrical as well as complementary pairs of P-type and N-type MOSFETs. | The NMOS performs its operation by making an inversion layer within a Ptype substrate. |
| Logic level | The logic level of CMOS is 0 V / 5 V. | The logic level of NMOS depends on the β ratio as well as noise margins. |
| Layout | CMOS has more regular layout. | NMOS has irregular layout. |
| Power dissipation | In case of CMOS, the power dissipation is zero, when it is in standby mode. | The power dissipates in NMOS, when its output is zero (0). |
| Power supply | For CMOS, the power supply may vary from 1.5 V to 15 V. | For NMOS, the power supply is fixed depending on VDD. |
| Packing density | CMOS has less packing density. Where, it requires 2N devices for N inputs. | The packing density of NMOS is high. It requires (N+1) devices for N inputs. |
| Load to drive ratio | CMOS has load / drive ratio 1:1 or 2:1. | NMOS has load / drive ratio 4:1. |
| Transmission gate | The transmission gate of CMOS allows to pass both ‘0’ and ‘1’ logic well. | The transmission gate of NMOS allows to pass only the logic ‘0’ well. If it pass logic ‘1’, then it will have VT drop. |
| Static power consumption | CMOS consumes low static power. | NMOS consumes relatively more static power. |
| Noise immunity | CMOS has high noise immunity. | NMOS has comparatively low noise immunity. |
| Applications | The CMOS is used to design various types of digital logic circuits, microprocessors, microcontrollers, memories, etc. | NMOS is used to design several types of digital logic circuits such as microprocessors, memory chips, and many other MOS devices. |
Conclusion
From the above comparison, it is clear that the CMOS technology is best suited for designing embedded systems. The one most significant difference between CMOS and NMOS is that the CMOS consumes low static power as compared to NMOS.
Why
do we use CMOS instead of PMOS and NMOS?
An
advantage of CMOS over NMOS logic is that both low-high and high-low output
transitions are fast since the on-state (PMOS) pull-up transistors are in
contrast to the load resistors in NMOS logic have a low resistance. In
addition, the output signal oscillates the full voltage between low and high rail.

Comments
Post a Comment